* MD5 digest(message digest type 5) is used by default.
1
www.ncpnetwork.com | www.ncpnuggets.in info@ncpnetwork.com
+919871 48 1152 | +919910 111 641
Syllabus CCNP Enterprises
Network Terminology
• Route Selection Component
• LM
• AD
• METRIC
• Route Tagging
• Route filtering
• Route Poisson
• Auto Summary
• Manual Summary
• PBR
• VRF
• BFD
EIGRP
• Eigrp Introduction
• EIGRP Implementation
• Types of Eigrp Tables
• Neighbor Adjacency Component
• Eigrp Neighbor Table Explain
• Eigrp packet capture with Wireshark
• Eigrp authentication & Verification with Wireshark
• Eigrp Auto-Summary
• Eigrp Manual summary
• Eigrp no-summary
2
• DUAL & Its Component
• Successor, feasible successor, RD and, AD
• Load distribution on un-equal path via Variance Factor
• Route filtering via ACL & Distribute List ( inbound and outbound)
• Route filtering via Prefix-list (Inbound and Outbound)
• Eigrp Internal Default Route
• Eigrp external Default Route
• Eigrp Split-Horizon
• Eigrp unicast behavior
• Route Tagging & Filtering with route_map
• EIGRP route poison
• SIA (Stuck in Active)
• SIA Quarry, SIA Reply
• Eigrp STUB Feature
• Eigrp Address Family
• Named Eigrp
OSPF
• OSPF Introduction
• OSPF Implementation
• OSPF Metric type 1 & type 2 Modification & Verification
• OSPF Cost Calculation
• OSPF Neighbor Adjacency Component.
• Types of OSPF Network
✓ point to point
✓ point to multipoint
✓ BMA & NBMA
• OSPF Authentication and Verification with Wireshark
• Hello and Dead Timer Mismatch
OSPF AREA Types
✓ Normal
✓ STUB
✓ NSSA
• Types of OSPF Routers
• Internal, External, Backbone, ABR, ASBR, DR, BDR
• Election Process of DR & BDR
3
• Function of wait timer in DR & BDR
• Summarization and ABR / ASBR
• OSPF Redistribution
• OSPF Database
• LSA TYPE-1, LSA-2 , LSA-3, LSA-4, LSA-5, LSA-6, LSA-7
• AGE, SEQ NO. LINK Count.
• LSA Refresh Timer
• STUB Area, Totally Stub Area, NSSA, Totally NSSA
• OSPF Default Route in normal Area
• OSPF Default Route in NSSA
• NSSA will not allow LSA Type 5
• OSPF Path Preference
✓ O vs OIA
✓ OE1 vs OE2
✓ OE2 vs ON2
✓ OIA vs ON2
• OSPF Loopback as a host Route
• OSPF Virtual- link
• Route filtering
• ACL & Distribute-list
• Prefix & Distribute-list
• OSPF Packet Types Verification with Wireshark
• OSPF Route State Verification with Wireshark & Debug
BGP
• BGP Introduction
• Protocol & Port no.
• Types of BGP Table
• Types of ASN
✓ Public ASN
✓ Private ASN
• BGP 2Byte ASN
• BGP 4 Byte ASN
• Types of Neighbor
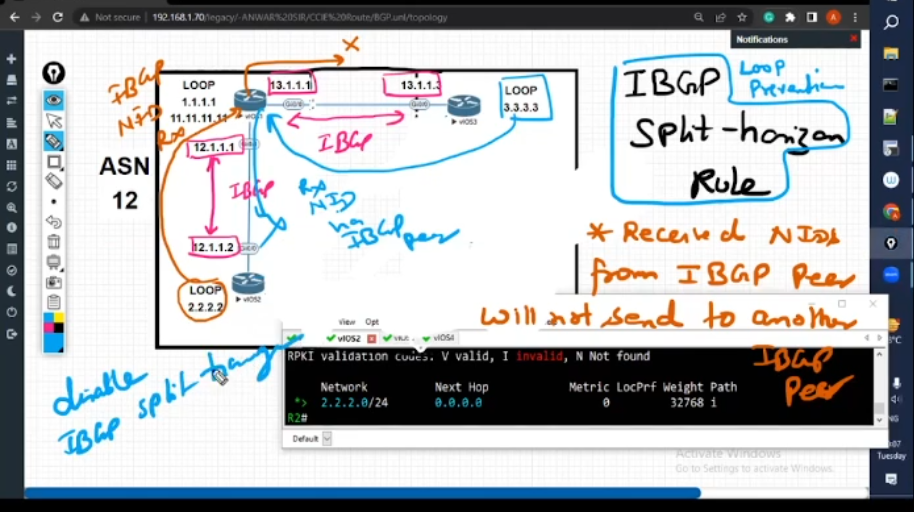
• IBGP Peer
• EBGP Peer
4
• BGP Neighbor Adjacency Component
• When BGP Neighbor will not form
• Explain of “show ip bgp summary”
• Verification of TCP Connection
• Explain “show ip BGP”
• IBGP & EBGP Peer on common subnet
• Concept of update source loopback
• Concept of EBGP Multiple hop
• Concept of TTL Modification IBGP & EBGP
• Next hop will change in EBGP
• BGP Authentication
• Next hop self
• IBGP Synchronization rule
• IBGP loop prevention technique
• IBGP Split-horizon rule
• Route-reflector–client
• Originator ID
• Cluster ID
• BGP Route filtering
• BGP path selection order
• BGP Traffic Policy
✓ Incoming traffic policy
✓ Outgoing traffic policy
• Verification of default outgoing path
• Modification of outgoing path via Weight & Attributes
• use of ACL / Prefix & Route-map
• Modification of outgoing path via LP
• Verification of default incoming path
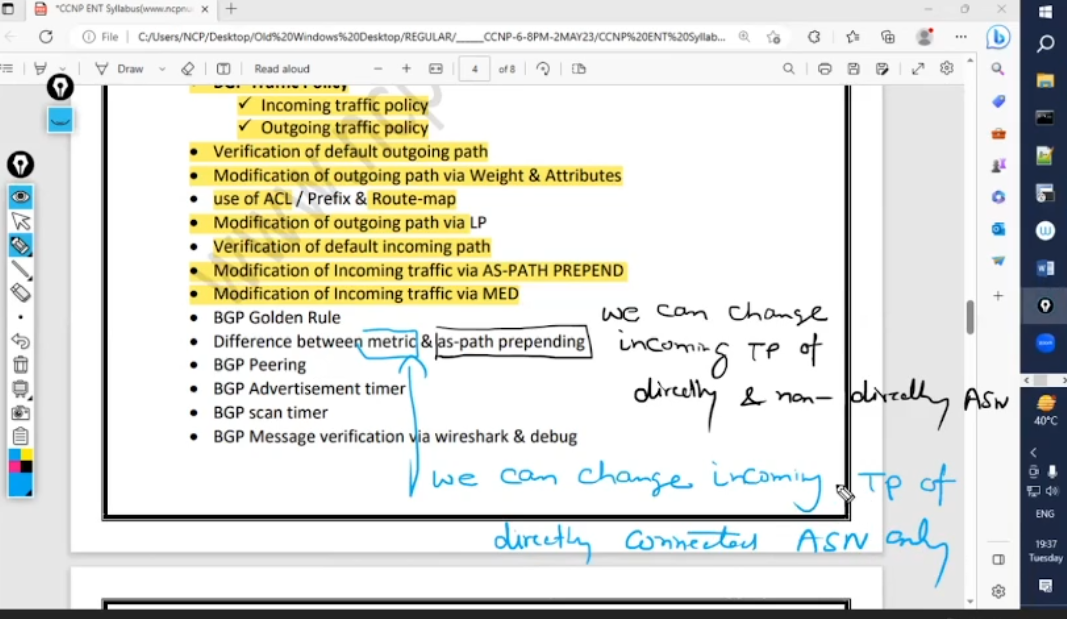
• Modification of Incoming traffic via AS-PATH PREPEND
• Modification of Incoming traffic via MED
• BGP Golden Rule
• Difference between metric & as-path prepending
• BGP Peering
• BGP Advertisement timer
• BGP scan timer
• BGP Message verification via wireshark & debug
5
• TCP session/BGP session Tracking of Neighbor
• BGP Confederation
• Remote private ASN
• EBGP Loop prevention Technique
• BGP route-refresh
• BGP Aggregate
• BGP Route-State
• BGP State
• BGP Dynamic peer
• BGP Address family
DMVPN
• MGRE
• NHRP
• NHRP Registration & Reply
• Under lay & over lay Network
• NHRP Server & Client
SECURITY
• UPRF
• UPRF Mode
✓ stick mode
✓ loose Mode
• Control Plain Policy
• Telnet
• SSH
• SNMP
• EIGRP
• OSPF
• BGP
IPV4 Access-list
• Standard
• Extended
• Time-based
IPV6 Traffic Filter
6
AAA
• Radius vs Tacacs+
• AAA Configuration
• IPV6 First hop Security
IPV6
• Ipv6 Introduction
• IPv6 Rules
• Types of IPv6 Address
• IPv6 Host Bits and Network bits
• IPv6 EUI-64
• IPv6 address Implementation and Verification
• IPv6 OSPF V3
• IPv6 EIGRP v6
• IPv6 BGP
• IPv6 Static Route
• IPv6 RIP
• IPv6 Protocol Redistribution
VPN
VPN Introduction
VPN Model
Classification of VPN
VPN Terminology (GRE)
GRE
Drawback of GRE
VRF
VRF Implementation (static)
VRF Lite
MPLS Introduction
MPLS Architecture
Control Plain and Data plain
LDP lable allocation & Distribution
LDP label operation (push, swap, pop)
7
IPSEC VPN
• Encapsulation
• encryption
• Hashing
• DH GROUP
SERVICES
• syslog server
• Types of syslog server
• consol login
• Terminal login
• syslog server login (external server)
• syslog severity level
IPv6 DHCP Server
• client
• Relay agent
• packet
SCP (Secure copy)
SNMP
SNMP Message
SNMPv3 Authentication
SNMPv3 Configuration
PBR + IPSLA
Net-flow
Device Management
Address Family
• EIGRP with Named
• EIGRP with address family IPv4
• EIGRP with address family IPv6
• OSPF with address family IPv4
• OSPF with address family IPv6
• BGP with address family IPv4
• BGP with address family IPV6




Comments
Post a Comment
I GOT YOUR POINT